HEAT EXCHANGER
Heat exchanger is a device typically used to transfer “exchange” heat from one state to another or between two or more fluids. When fluid is used to transfer a heat, it could be a liquid, such as water or oil, or could be moving air
Heat exchangers are only used for heating applications, such as space heaters, but also using in cooling application such as refrigerators and air conditioner.
Based on the direction of liquid flow the type of heat exchanger are differ in such application heat exchangers can have a three flow of direction
- Parallel flow-> In parallel flow both fluid move in same direction entering and exiting of fluid in the exchanger side by side.
- Cross flow-> In cross flow the exchanger fluid path runs perpendicular to each other.
- Counter flow-> Its move effective way the fluid paths flow in opposite direction each exiting where the other enters.
The fluid may be separated by a soild wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact.

APPLICATIONS OF HEAT EXCHANGER:
Heat exchangers are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural gas processing and sewage treatment.
Hydraulic oil cooler are example will remove heat from hot oil by using cold water or air.
Swimming pool heat exchanger use a hot water from boiler or solar heated water circuit to heat the pool water.
“Car Radiator” is a well known type of heat exchanger. In radiator, a solution of water, the ethylene glycol, also known as antifreeze is to transfer a heat from the engine to the radiator and then from the radiator to the ambient air flow through it, this process helps to keep a car engine from over heating.
THE BASIC DATA TO DESIGN A HEAT EXCHANGER:
- First known the primary circuit fluid type,(usually the hot fluid)and its temperature and flow rate of fluid.
- To exchange from a primary circuit fluid(Heat dissipation) or a target outlet temperature.
- Secondary fluid type, required temperature and flow rate(usually the coolant)
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN HEAT EXCHANGER AND HEAT EXTRACTOR
HEAT EXTRACTOR -> In our home extractor fan is used in kitchen or in bathroom is designed to suck hot, moist air from home and dump it outside. Heat extractor it take one fluid (hot air in your home) mixes it with another one (cold air in outside).
HEAT EXCHANGER->Heat exchanger is a device typically used to transfer “exchange” heat from one fluid to another fluid.
HVAC System for a heat exchanger:
Heating, ventilation and air conditioning system provides thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC air coils, liquid to air, or air to liquid HVAC coils are modified cross flow arrangement. In vehicles heat coils are often called as heat cores.
TYPE OF HEAT EXCHANGER
- Shell and Tube heat exchanger
- Plate heat exchanger
- Plate and Shell heat exchanger
- Adiabatic Wheel heat exchanger
- Plate and fin heat exchanger
- Pillow plate heat exchanger
- Fluid heat exchanger
- Waste heat recovery unit
- Dynamic scraped surface heat exchanger
- Phase change heat exchanger
- Direct contact heat exchanger
- Micro channel heat exchanger
SHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER:

Shell and tube heat exchanger are frequently used type of heat exchanger in industrial field. It has a series of tubes are through which liquids are flow. The tubes can be divided into two sets, one set of tube can a fluids it can be either heated or cooled. The second set contains the liquid responsible for triggering the heat exchange, either absorb a heat from the first set of tubes or transmitting the heat, cooling the liquid or warming the liquid by transmitting a liquid its own heat to the liquid inside.
A set of tubes is called the tube bundle and can be several types they are longitudinally, plain and finned etc. while designing a shell and tube heat exchanger there are several type thermal design features may be consider. Each tubes in shell and tube heat exchanger are connected to plenums (sometime called water boxes) through holes in tube sheets. The tube may be bent in shape U called U-bundle or straight tubes.
While designing shell and tube heat exchanger mainly focus on the following items are listed
- Tube Diameter
- Tube Thickness
- Tube length
- Tube pitch
While designing shell and tube heat exchanger mainly focus on the following items are listed
- Tube corrugation
- Tube lay out
- Baffles design
PLATE HEAT EXCHANGER:
Plate heat exchanger consist of thin stainless steel plates are joined together with small space between the plates joined together are typically maintained by the small rubber gasket and brazing.
In HVAC applications, large heat exchangers of this type are used called plate and frame. Several types are bonded with plate heat exchanger they are
- Dip- brazed
- Vacuum –brazed
- Welded plate varieties often specified as closed loop application often used in refrigeration.
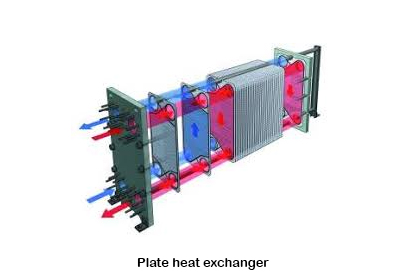
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN SHELL AND TUBE & PLATE HEAT EXCHANGER:
Shell and tube heat exchanger has a higher volume and cost. Plate heat exchanger has a low volume and cost.
Shell and tube heat exchanger serve medium to high pressure. Plate heat exchanger serves low to medium pressure.
Plate heat exchanger has a counter current flow, which allow low temperature difference, and increase efficiency. Shell and tube exchanger has a cross current flow.
PLATE AND SHELL HEAT EXCHANGER:
Plate and shell heat exchanger is the third type which is the combination of combination of plate exchanger and shell and tube exchanger process. The main process of heat exchanger contain a fully welded circulate plate pack made by pressing and cutting round plate and welding them together.
Inlet and Outlet of the plate pack the liquid flow carried by the nozzle. The outer shell of the fully welded plate pack which creates the second flow path (the “shell side”). Plate and shell technology offers high heat transfer, high pressure, high operating temperature. In particular, it closes completely without gaskets, which provides security against leakage at high pressure and temperature.
ADIABATIC WHEEL HEAT EXCHANGER:
The fourth type of heat exchanger is adiabatic wheel exchanger which uses intermediate (in between) fluid or solid state to hold heat which is then moved to the outer side of the heat exchanger to be released.
Adiabatic wheel has two examples consists of large wheel with fine threads rotating through the hot and cold fluids and fluid heat exchanger.
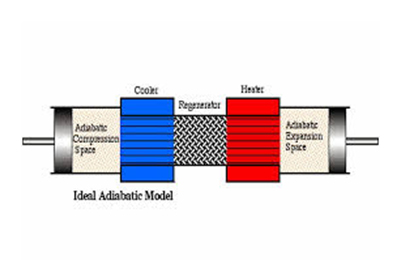
PLATE FIN HEAT EXCHANGER:
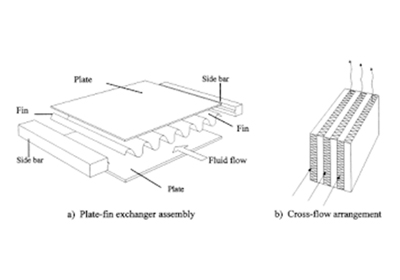
This type of heat exchanger flow of fluid through between the upper and lower layer of the plate containing fins to increasethe effectiveness of the unit.
The design of plate fin heat exchanger include both crossflow, counter flow coupled with various fins. Configuration suck as straight fins, offset finsand wavy fins. Plate fin heat exchanger has a high heat transfer efficiency because it usually made up of aluminium alloys. This enables the system to operate at a low temperature difference and reduce height of the equipment.
The transport industries, motors and aircraft engine use a plate and fin heat exchanger because it mostly used low temperature services such as natural gas helium and oxygen liquefaction plants.